Low Random Error Bullseye
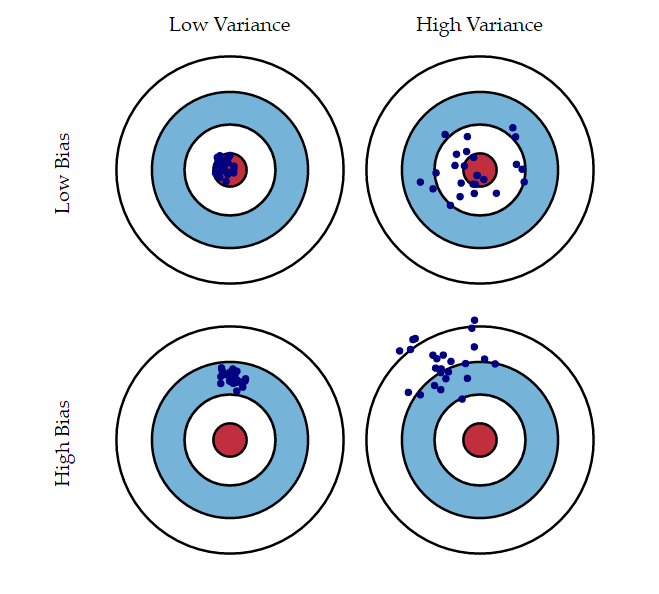
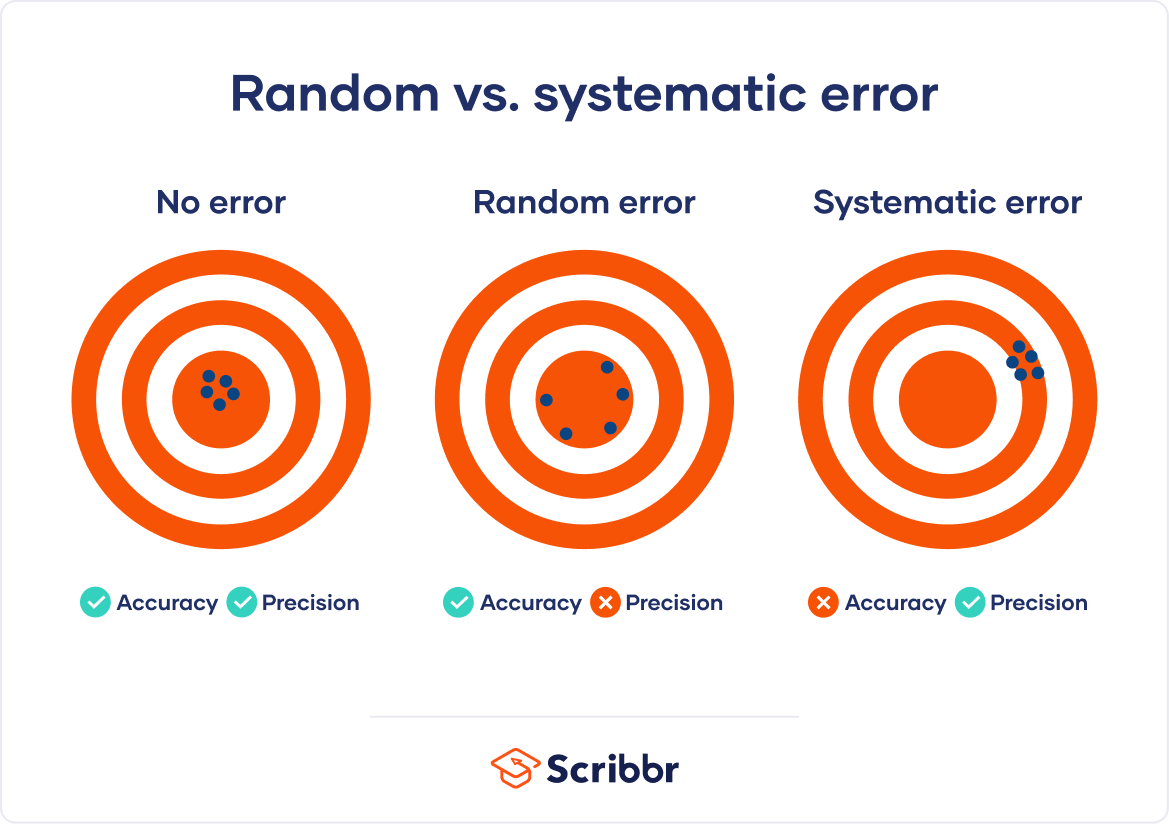
Low Random Error Bullseye - Systematic errors & random uncertainty quiz for grade students. Random error, also known as statistical error, is the unpredictability in measurement caused by unknown and unpredictable variations in the. Random errors are when you get a large variation in readings about a mean value when you take a measurement repeatedly. Random error (variability, imprecision) can be overcome by increasing the sample size. The ideal scenario where the darts are closely grouped around the bullseye. State how the significance level and power of a statistical test are related. This is illustrated in this section via hypothesis testing. Distinguish between random error and bias in collecting clinical data. Find other quizzes for physics and more on quizizz for free! Conversely, you could accidentally hit the bullseye once (accurate) but fail to do so consistently if there's a lot of random error or low precision.
Find other quizzes for physics and more on quizizz for free! Systematic errors & random uncertainty quiz for grade students. Conversely, you could accidentally hit the bullseye once (accurate) but fail to do so consistently if there's a lot of random error or low precision. A good analogy is with the grouping of a player’s darts on a dartboard, where the ideal target is the bullseye at the center of the board. This is illustrated in this section via hypothesis testing. The ideal scenario where the darts are closely grouped around the bullseye. State how the significance level and power of a statistical test are related. Random error, also known as statistical error, is the unpredictability in measurement caused by unknown and unpredictable variations in the. Random error (variability, imprecision) can be overcome by increasing the sample size. Random errors are when you get a large variation in readings about a mean value when you take a measurement repeatedly.
Random error, also known as statistical error, is the unpredictability in measurement caused by unknown and unpredictable variations in the. Find other quizzes for physics and more on quizizz for free! Conversely, you could accidentally hit the bullseye once (accurate) but fail to do so consistently if there's a lot of random error or low precision. Random errors are when you get a large variation in readings about a mean value when you take a measurement repeatedly. Distinguish between random error and bias in collecting clinical data. This is illustrated in this section via hypothesis testing. The ideal scenario where the darts are closely grouped around the bullseye. State how the significance level and power of a statistical test are related. Random error (variability, imprecision) can be overcome by increasing the sample size. A good analogy is with the grouping of a player’s darts on a dartboard, where the ideal target is the bullseye at the center of the board.
Error Bars, Max Min Line On The Graph IB Physics Chapter, 59 OFF
Random errors are when you get a large variation in readings about a mean value when you take a measurement repeatedly. A good analogy is with the grouping of a player’s darts on a dartboard, where the ideal target is the bullseye at the center of the board. Systematic errors & random uncertainty quiz for grade students. Find other quizzes.
Accuracy and Precision, Systematic and Random Error. With increasing
Conversely, you could accidentally hit the bullseye once (accurate) but fail to do so consistently if there's a lot of random error or low precision. The ideal scenario where the darts are closely grouped around the bullseye. Random error (variability, imprecision) can be overcome by increasing the sample size. Distinguish between random error and bias in collecting clinical data. Random.
Systematic Error vs. Random Error — What’s the Difference?
Conversely, you could accidentally hit the bullseye once (accurate) but fail to do so consistently if there's a lot of random error or low precision. Systematic errors & random uncertainty quiz for grade students. Random error (variability, imprecision) can be overcome by increasing the sample size. A good analogy is with the grouping of a player’s darts on a dartboard,.
Visualizing Random Measurement Error in R Steven V. Miller
Find other quizzes for physics and more on quizizz for free! Distinguish between random error and bias in collecting clinical data. Random errors are when you get a large variation in readings about a mean value when you take a measurement repeatedly. State how the significance level and power of a statistical test are related. This is illustrated in this.
1. Illustration of a random error and a systematic error according to
A good analogy is with the grouping of a player’s darts on a dartboard, where the ideal target is the bullseye at the center of the board. Random error (variability, imprecision) can be overcome by increasing the sample size. This is illustrated in this section via hypothesis testing. Conversely, you could accidentally hit the bullseye once (accurate) but fail to.
Systematic vs Random Error Differences and Examples
Random error (variability, imprecision) can be overcome by increasing the sample size. The ideal scenario where the darts are closely grouped around the bullseye. Random errors are when you get a large variation in readings about a mean value when you take a measurement repeatedly. A good analogy is with the grouping of a player’s darts on a dartboard, where.
Random vs. Systematic Error Definition & Examples
Conversely, you could accidentally hit the bullseye once (accurate) but fail to do so consistently if there's a lot of random error or low precision. State how the significance level and power of a statistical test are related. Distinguish between random error and bias in collecting clinical data. The ideal scenario where the darts are closely grouped around the bullseye..
Website Error Screen Free Stock Photo Public Domain Pictures
Conversely, you could accidentally hit the bullseye once (accurate) but fail to do so consistently if there's a lot of random error or low precision. State how the significance level and power of a statistical test are related. Random error, also known as statistical error, is the unpredictability in measurement caused by unknown and unpredictable variations in the. Random errors.
Random error occured for 3d time in row. r/OpenCoreLegacyPatcher
Distinguish between random error and bias in collecting clinical data. Random errors are when you get a large variation in readings about a mean value when you take a measurement repeatedly. Find other quizzes for physics and more on quizizz for free! Systematic errors & random uncertainty quiz for grade students. Random error (variability, imprecision) can be overcome by increasing.
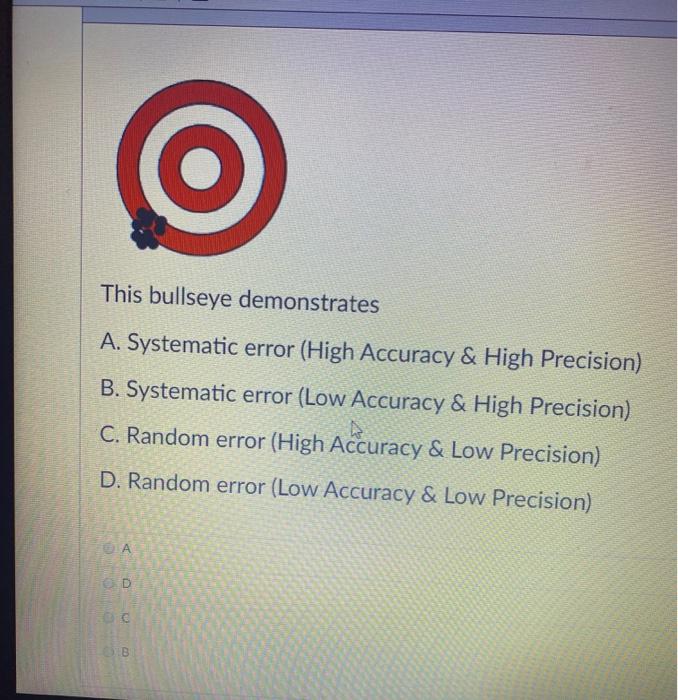
Solved This bullseye demonstrates A. Systematic error (High
Find other quizzes for physics and more on quizizz for free! Random error (variability, imprecision) can be overcome by increasing the sample size. This is illustrated in this section via hypothesis testing. Random errors are when you get a large variation in readings about a mean value when you take a measurement repeatedly. Systematic errors & random uncertainty quiz for.
Random Error, Also Known As Statistical Error, Is The Unpredictability In Measurement Caused By Unknown And Unpredictable Variations In The.
Systematic errors & random uncertainty quiz for grade students. Random errors are when you get a large variation in readings about a mean value when you take a measurement repeatedly. State how the significance level and power of a statistical test are related. The ideal scenario where the darts are closely grouped around the bullseye.
Random Error (Variability, Imprecision) Can Be Overcome By Increasing The Sample Size.
Conversely, you could accidentally hit the bullseye once (accurate) but fail to do so consistently if there's a lot of random error or low precision. Find other quizzes for physics and more on quizizz for free! This is illustrated in this section via hypothesis testing. Distinguish between random error and bias in collecting clinical data.